Should You Punish or Reward Current Customers?
Is it better to reward existing customers for loyalty — or spend your marketing dollars on attracting new ones? Here is a framework to help you decide.
Topics
Charlie, a loyal customer of his local bank, had never thought of taking his business elsewhere, but the offer from a competing bank to refinance his mortgage at an extremely low interest rate seemed too good to pass up. He asked Rick, the loan officer he had been dealing with for years, if the bank could match the offer. Rick knows lowering Charlie’s mortgage rate won’t be good for the bank’s bottom line, but he thinks making a long-time customer happy is worth the investment. Should the bank match the offer, or should it let Charlie go?
This anecdote, while fictional, represents a real customer management dilemma faced by many companies nowadays: Should we offer better deals to current customers or to new ones? In particular, at what cost should we keep current customers, as opposed to seeking out new ones? The question is simple, but the answer is not.
A quick scan of offers found in the marketplace does not reveal obvious commonalities and provides little insight. While airlines give lavish frequent-flyer packages to their most loyal customers, wireless carriers generally focus on wooing new customers through introductory deals. Hotels often do both. Apparel catalog retailers send special discount “value” catalogs to existing customers, whereas magazines, newspapers and software companies often offer discounts to new customers by offering them lower introductory prices.
But would it, for example, be more profitable for a newspaper to offer a better price for subscription renewal rather than new subscriptions? Should a wireless carrier instead offer lower rates to its high-volume customers who have stayed with the carrier for a long time? Should a hotel, airline or retailer offer better rates to new customers it aims to acquire? Ultimately, how can a manager reconcile the demands of current customers with the need to
attract new customers?
Expert opinions on this subject conflict. On one side, you can find people who argue that careful attention to the needs of existing customers like Charlie deepens the relationship between customer and company. That, in turn, leads to continuous increases in customer satisfaction, loyalty and company profitability in a virtuous cycle of mutual benefits. Customers get better rewards, and the companies get more business from those customers.1 People who take this position are quick to point out the basic and well-established fact that customer retention is notably less expensive than acquisition. This consumercentric view presumes that a loyal customer is a good customer deserving of rewards.
On the other side, you can find people who take a company-centric perspective, one that is skeptical of customer-centric narratives and conventional wisdom. Essentially, their argument is this: Simply by virtue of purchasing from and being loyal to a company, existing customers have revealed that they much prefer the company’s products or services to those of competitors. Therefore, they argue, existing customers should be “punished” with higher prices than new customers receive, given their willingness to pay them in the past, and companies should focus their rewards and incentives on new customers in an attempt to increase sales and earnings.2
Our view is that to create an artificially stark dichotomy — you should always reward or punish your own customers or new customers — is a misleading black-and-white simplification. Both arguments have merit; the appropriateness of each strategy depends on the circumstances a company faces. What this means is that executives need a framework for deciding the best way to increase maximum profitability. Our recent research provides one.3 (See “About the Research.”)
Flexibility and Value Concentration
In structuring our framework, we introduce two basic rules characterized by simple but often ignored features of customer behavior. First, consumers’ preferences for a product often change depending on the purchase occasion. Such changes in preferences can happen independent of marketing or pricing, because consumers’ needs or wants depend on the specifics of each purchase occasion.
For example, a customer may generally prefer a Lowe’s store for home improvement products because it is closer to her home and, in her opinion, offers superior quality offerings. However, she may still prefer to go to The Home Depot on the drive home from the office because it is more convenient to her route. We define this fluidity of customer preferences as shopping flexibility.
This flexibility is not restricted to store choice and geographic location. Consider a college student who lives in New York. He generally prefers American Airlines because he likes its service and it flies a direct route to his hometown. However, when he needs to visit a friend in Houston, Texas, he may prefer United Airlines because it has more direct flights for that route.
The second feature of customer behavior that is important to understand in resolving the “reward or punish” dilemma is the fact that, in many markets, not all customers are equally valuable. Some contribute far more to a company’s profits than others. An American Express executive, for example, once reported that the best customers outspent others by 16 to 1 in retailing, 13 to 1 in restaurants, 12 to 1 in airlines and 5 to 1 in hotel/motels.4 These are examples of the widely known (and empirically supported) 80-20 rule, with a small number of customers (20%) contributing a large amount of profit (80%).5 We define this imbalance as value concentration.
Over the past two decades, massive investment in organizational resources (human, technical and financial) to build information infrastructures that store and analyze data about customer purchase behavior has helped unearth the details of value concentration. Armed with this data, companies can pursue fine-grained microsegmentation and customer management strategies. However, even with all this data, companies continue to differ on whether they offer a lower price to their own customers or competitors’ customers, and the question of when such segmentation and differential pricing is profitable remains open.
When to Reward or Punish
In our research, we found that these two basic customer dimensions of shopping flexibility and value concentration provide insight into how managers might best balance customer retention and acquisition. Specifically, we discovered that, most of the time, rewarding and acquiring new customers creates the most value. Under select circumstances, however, attention should shift to the retention of existing high-value customers. We recommend that managers choose their approach based on these two features. (See “Identifying the Best Customer Management Strategy.”) In markets that have a high degree of both flexibility and value concentration, companies should focus on rewarding their own customers — in particular, their best customers. If either of these characteristics is not in place — that is, either the value concentration is low, shopping flexibility is low or both are low — then managers should focus on rewarding new customers or those drawn from the competition.
Identifying the Best Customer Management Strategy
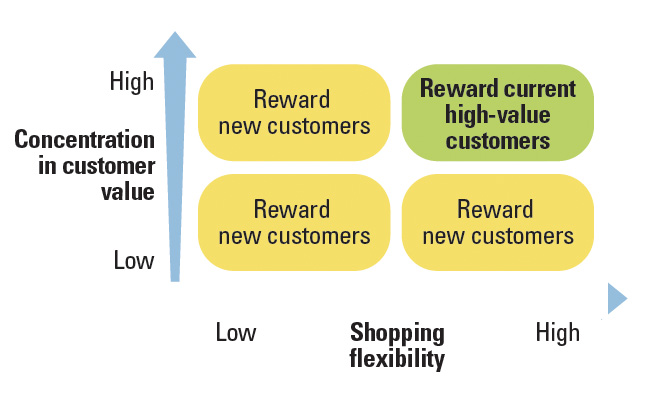
Returning to some of our specific examples in the introduction will help us to understand the logic behind these recommendations. Consider magazine subscriptions, where both value concentration and shopping flexibility are quite low: Most subscribers buy only one subscription per periodical (low value concentration), and they typically purchase subscriptions for an extended length of time, often six months or a year (low shopping flexibility). Given the combination of low value concentration and low shopping flexibility, the camp that advocates investing in customer acquisition is indeed right, and we recommend that managers focus on rewarding new customers with introductory offers.
Next, consider the case of cellphone contracts. Here, there is low shopping flexibility but a greater degree of value concentration. Cellphone contracts often run for one to two years, but consumer usage varies substantially. Phone service providers offer different plans at different tiers, and users contribute very different amounts of revenue to a company. In this case, despite the higher levels of concentration, the low degree of shopping flexibility ensures that it is optimal for cellphone companies to focus on acquiring new customers, since it is not easy for their existing customers to switch to the competition.
Indeed, this tactic is generally on display in the introductory contract deals offered by cellphone companies: reduced monthly rates for a fixed period of time, free phones and often an offer to pay the contractual fees incurred by customers who leave their current carriers. On the other hand, cellphone companies are quick to punish existing customers by raising monthly rates midcontract, and customers renewing a contract typically do not get the lower introductory rates. They might get a small discount on a new phone, but even here, the discount is less than a new customer typically receives.
Finally, consider the case of retail stores, which typically are characterized by high degrees of both shopping flexibility and value concentration. In retail, for example, different people spend vastly different amounts on clothes and can switch from store to store at the drop of a hat. As per our framework, with both conditions (a high degree of shopping flexibility and a high degree of value creation) met, retailers should reward and focus on retaining existing customers by providing discount value catalogs or membership club cards to frequent, high-value shoppers. When there is a high degree of value concentration, it is important to retain those high-value customers; otherwise, you are endangering profitability.
That’s especially true where there is a good chance of customer switching due to high shopping flexibility, such as exists in the rental car industry, another industry in which the best customers can outspend the rest substantially. Indeed, the best incentives and rewards in the car rental markets are reserved for existing customers. The same is also true of airlines, where it is generally agreed that the top customers fly disproportionately more and pay higher prices, creating a substantial concentration in customer value.
Which Customers Should You Reward?
If you decide to reward existing customers in markets with high shopping flexibility and high value concentration, another series of important, related questions remains: Should every existing customer be rewarded? And, if not, then which existing customers should be rewarded, and how might one select them?
The answer to the first question fits business intuition: To make sure their most profitable customers stay with them, companies should selectively reward the most profitable customers, as they contribute most to the customer value concentration. And indeed, business practices are consistent with implications from our analysis: Retailers, car rental companies and airlines selectively reward their most profitable customers, who are at the core of customer value concentration. These are industries with tiered loyalty programs — like the airlines’ frequent flyers clubs — where there is substantial differentiation in the services and incentives provided to higher-loyalty tiers.
While selectively rewarding the most profitable customers makes intuitive sense, it is not necessarily obvious how to identify those customers, or what to do about customers who are not particularly profitable. Consider the following examples:
- a Netflix customer who is paying a modest fee to receive DVDs by mail, yet rents many DVDs per month;
- a bank customer who insists on visiting the bank multiple times a month and never uses ATMs or online services;
- a retail customer who buys numerous items with the intent to return most of them; and
- a business customer who exploits free delivery to order small quantities and thus minimize his inventory costs.
In all these examples, revenues and profits may not necessarily be correlated. In the examples above, a customer can receive a suite of services as part of a purchase. Customers who use these services excessively can be very unprofitable, while those who use these services sparingly can be highly profitable. This raises the obvious question: Does it make sense to retain those high-volume customers who also demand a great deal of service? It is not only possible that high-volume customers may not be as valuable as they seem, but, in some settings, they may be downright unprofitable. One study found that, in business-to-business companies, the top 20% of customers are generally responsible for 150%-300% of total profits, while the company breaks even on the middle 70% of customers and the bottom 10% of customers cause losses.6 Similarly, a multi-industry study by McKinsey & Co. found that bad customers might account for 30%-40% of a typical company’s revenue.7
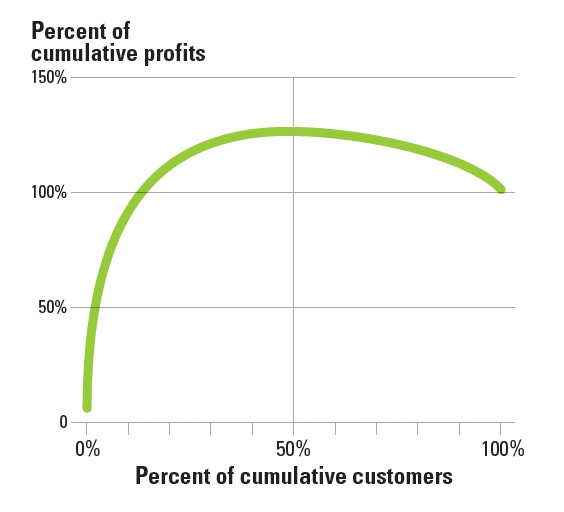
As an illustration, we provide the cumulative profits curve at a bank with which the second author has worked. (See “Many Customers Aren’t Profitable.”) This type of curve is often referred to as the “whale curve” because of the profit curve’s humpback, inverse-U shape.8 In this bank’s case, about 50% of customers contribute negatively to profits. In fact, the top 5% of customers contribute almost 75% of the bank’s profits.
Many Customers Aren’t Profitable
Given the fact that in some industries a select group of customers accounts for the vast majority of profits and other customers actually detract from company profits due to their high cost to serve, another question arises: Would it ever be appropriate to let some consumers go, or even proactively “fire” existing customers?
Sprint Nextel generated a flood of adverse publicity when, in 2007, it wrote a letter to some of its high-cost customers who contacted customer service very often — in Sprint’s view, too often. The key part of the letter stated: “The number of inquiries you have made to us during this time has led us to determine that we are unable to meet your current wireless needs. Therefore after careful consideration, the decision has been made to terminate your wireless service agreement.”9 The move created adverse publicity after it was widely reported.
We recognize the mix of concerns, both ethical and practical, that swirl around firing customers. Ethically, there may be issues about the fairness of focusing retention on the most profitable customers. Practically, there are a number of problems immediately associated with this tactic: negative opinions passed on to prospective customers, bad publicity, a social media firestorm and so forth. As a result, we advocate firing customers only as a last resort.
There are many potential steps you can take before reaching that point. Fidelity Investments, for example, some years ago educated a group of customers to use less costly service channels, such as the company’s website, rather than calling a customer service representative.10 Royal Bank of Canada simply reduced services to unprofitable customers. A check trace for profitable customers would be prioritized and expedited in one day, for example, while for unprofitable customers, the bank would conduct a less expensive three- to five-day trace.11
Education, particularly in business-to-business settings, is an especially valuable tool. If an explicit conversation can illustrate that both parties could save money with more economical behavior, then this is the easiest and best solution. In business-to-business industries, it is often useful to have a conversation with the customer, explaining which activities drive up costs and make the customer unprofitable to the supplier. For example, a customer who often cancels orders, requests expedited delivery or orders in very small batches can be extremely costly to the supplier. Highlighting how these types of customer behavior increase supplier costs and encouraging the customer to avoid such behavior can often lead to desired and profitable behavior on the part of the customer.
If such conversations are not effective, a supplier may need to charge separate fees for such costly services to rein in the undesirable behavior and convert the customer into a profitable one. And, of course, extraneous costs can be shifted from the company balance sheet to the consumer, thereby making unprofitable customers more valuable. For instance, some banks have started charging for paper statements while offering e-statements for free — a pricing enticement toward more profitable behavior among all customers.
But if these types of measures fail, and if customer cost-to-serve is very large, then it can pay to selectively raise prices for high-cost customers.12 That move will have two benefits. Some “bad” customers will leave the company. They will be, in effect, voluntarily “fired” by refusing to pay the higher price. And those bad customers who choose to stay will become more profitable.
The common apprehension among managers that firing customers may lead to allocating fixed service costs among fewer customers (making them unprofitable) is misplaced. The way around the concern is simple. Simultaneously with firing bad customers, the company should go out and obtain new customers — customers who are on average more profitable than the ones who were fired.
We find that the cumulative profits curve (“whale curve”) generally becomes progressively “flatter” over time when companies optimally manage customer acquisition and retention — in other words, retaining their most valuable customers while getting rid of the costliest customers and replacing them with new customers. When the curve is flatter, it indicates more equitable contribution to profits across customers. A company no longer suffers from bad customers generating losses within its own customer base.
We suggest that managers observe progressive flattening of the “whale curve” as a useful diagnostic to assess the efficacy of a company’s customer management strategies over time. Also, in assessing acquisition and retention strategies, managers must direct their attention and resources to the rate at which this whale tail flattens. Understanding how to use this analysis will help companies develop a more effective and profitable customer management strategy.
References
1. L. O’Brian and C. Jones, “Do Rewards Really Create Loyalty?” Harvard Business Review 73, no. 3 (May-June 1995): 75-82; and D. Peppers and M. Rogers, “Managing Customer Relationships: A Strategic Framework,” 2nd ed. (Hoboken, New Jersey: John Wiley & Sons, 2011).
2. D. Fudenberg and J. Tirole, “Customer Poaching and Brand Switching,” RAND Journal of Economics 31, no. 4 (winter 2000): 634-657; J.M. Villas-Boas, “Dynamic Competition With Customer Recognition,” RAND Journal of Economics 30, no. 4 (winter 1999): 604-631; and D. Fudenberg and J.M. Villas-Boas, “Behavior-Based Price Discrimination and Customer Recognition,” chap. 7 in “Economics and Information Systems,” ed. T.J. Hendershott, vol. 1 in “Handbooks in Information Systems,” (Bingley, United Kingdom: Emerald Group Publishing, 2006), 377-436.
3. J. Shin and K. Sudhir, “A Customer Management Dilemma: When Is It Profitable to Reward One’s Own Customers?” Marketing Science 29, no. 4 (July-August 2010): 671-689.
4. D. Peppers and M. Rogers, “The One-to-One Future: Building Relationships One Customer at a Time” (New York: Currency Doubleday, 1993).
5. D.C. Schmittlein, L.G. Cooper and D.G. Morrison, “Truth in Concentration in the Land of (80/20) Laws,” Marketing Science 12, no. 2 (spring 1993): 167-183.
6. R.S. Kaplan and V.G. Narayanan, “Measuring and Managing Customer Profitability,” Journal of Cost Management 15 (September-October 2001): 5-15.
7. R. Leszinski, F.A. Weber, R. Paganoni and T. Baumgartner, “Profits in Your Backyard,” McKinsey Quarterly no. 4 (November 1995): 118–127.
8. Kaplan and Narayanan, “Measuring and Managing Customer Profitability.”
9. M. Reardon, “Sprint Breaks Up With High-Maintenance Customers,” CNET News, July 5, 2007, http://news.cnet.com.
10. V. Mittal, M. Sarkees and F. Murshed, “The Right Way to Manage Unprofitable Customers,” Harvard Business Review 86, no. 4 (April 2008): 94-102.
11. L. Selden and G. Colvin, “Angel Customers & Demon Customers” (New York: Penguin Group, 2003), 157-158.
12. J. Shin, K. Sudhir and D. Yoon, “When to ‘Fire’ Customers: Customer Cost-Based Pricing,” Management Science 58, no. 5 (May 2012): 932-947.
i. Shin and Sudhir, “A Customer Management Dilemma”; and Shin, Sudhir and Yoon, “When to ‘Fire’ Customers.”


 View Exhibit
View Exhibit View Exhibit
View Exhibit
Comments (2)
Ajit Mathur
John Parisi